EXCRETORY SYSTEM
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The dual function of excretory systems is the elimination of the waste products of metabolism and to drain the body of used up and broken down components in a liquid and gaseous state. In humans and other amniotes (mammals, birds and reptiles) most of these substances leave the body as urine and to some degree exhalation, mammals also expel them through sweating.Only the organs specifically used for the excretion are considered a part of the excretory system. In the narrow sense, the term refer to the urinary system. However, as excretion involves several functions that are only superficially related, it is not usually used in more formal classifications of anatomy or function.As most healthy functioning organs produce metabolic and other wastes, the entire organism depends on the function of the system.
Urinary System
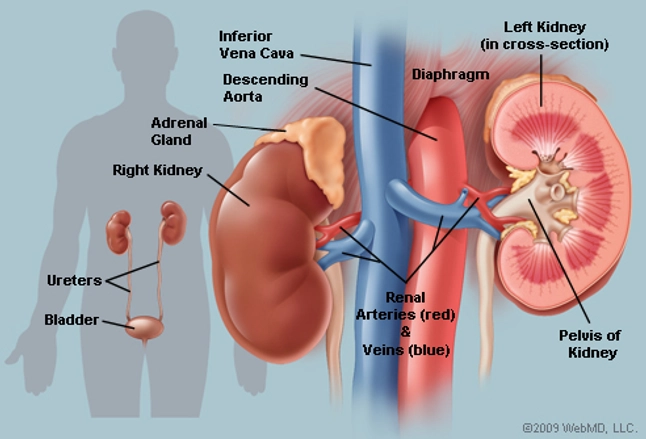
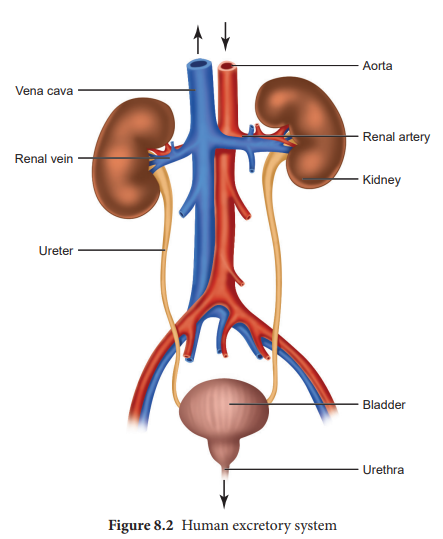
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It removes toxic materials from the blood to produce urine, which carries a variety of waste molecules and excess ions and water out of the body.
The kidneys are large, bean-shaped organs which are present on each side of the vertebral column in the abdominal cavity. Humans have two kidneys and each kidney is supplied with blood from the renal artery. The kidneys remove from the blood the nitrogenous wastes such as urea, as well as salts and excess water, and excrete them in the form of urine. This is done with the help of millions of nephrons present in the kidney. The filtrated blood is carried away from the kidneys by the renal vein (or kidney vein). The urine from the kidney is collected by the ureter (or excretory tubes), one from each kidney, and is passed to the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder collects and stores the urine until urination. The urine collected in the bladder is passed into the external environment from the body through an opening called the urethra.
Kidney
The kidney's primary function is the elimination of waste from the bloodstream by production of urine. They perform several homeostatic functions such as:-- Maintain volume of extracellular fluid
- Maintain ionic balance in extracellular fluid
- Maintain pH and osmotic concentration of the extracellular fluid.
- Excrete toxic metabolic by-products such as urea, ammonia, and uric acid.
The way the kidneys do this is with nephrons. There are over 1 million nephrons in each kidney; these nephrons act as filters inside the kidneys. The kidneys filter needed materials and waste, the needed materials go back into the bloodstream, and unneeded materials become urine and are gotten rid of.
Uterer
The ureters are muscular ducts that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the human adult, the ureters are usually 25–30 cm (10–12 in) long. In humans, the ureters arise from the renal pelvis on the medial aspect of each kidney before descending towards the bladder on the front of the psoas major muscle. The ureters cross the pelvic brim near the bifurcation of the iliac arteries (which they run over).
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects waste excreted by the kidneys prior to disposal by urination. It is a hollow muscular, and distensible (or elastic) organ, and sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
Urethra
In anatomy,it is a tube which connects the urinary bladder to the outside of the body. In humans, the urethra has an excretory function in both genders to pass.
Post a Comment